View Large
View Large
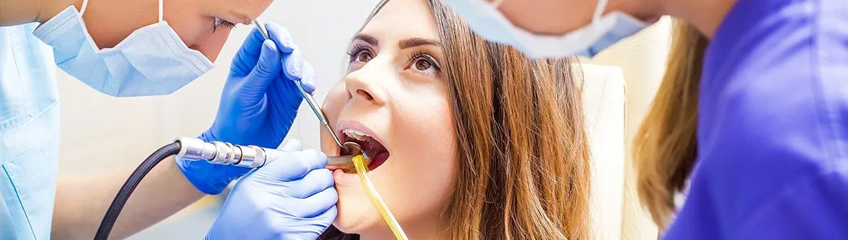
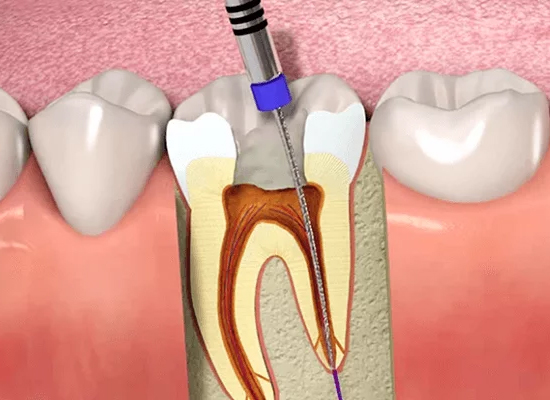
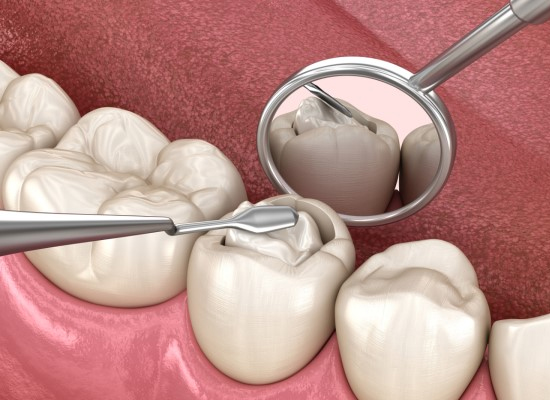
Laser Dentistry
You can have to pay thousands of dollars for restorative dental care if you don’t take good care of your teeth and maintain good oral hygiene. The cost of a full mouth reconstruction can range as you may not be aware. Preventive dentistry is your best defence against these outrageous dental bills.
In order to avoid tooth decay and other dental diseases and problems, preventive dentistry places a strong emphasis on the necessity of regular hygiene practices and daily habits. In order to achieve effective preventive dentistry, patients should combine chairside treatments and counselling with at-home oral hygiene practices.
The American Dental Association (ADA), for instance, advises having at least two annual dental examinations for professional cleaning and treatment of any emerging issues. By following this advice, you may assist your dentist in preventing dental disease before it becomes serious, saving you money and safeguarding your smile.
Preventive Dentistry Strategies
Various in-office and at-home care activities are part of preventive dental care methods for both adults and children. These include:
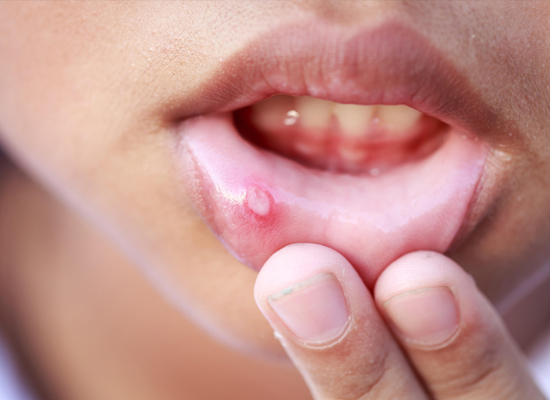
oral hygiene practices at home. The most crucial preventive method is to remove dental plaque, which is a film-like covering that develops on your teeth, by brushing and flossing at least twice a day (or after every meal). Dental tartar, a hardened, sticky substance containing acid-producing bacteria that cause tooth decay and eventually lead to gum disease, is created when plaque builds up and is not removed.
Eat a diet. A healthy diet is crucial for dental health. Sugary and carbohydrate-rich foods nourish the bacteria that cause dental plaque, and diets low in calcium raise your risk of periodontal disease, or gum disease, and jaw degradation.
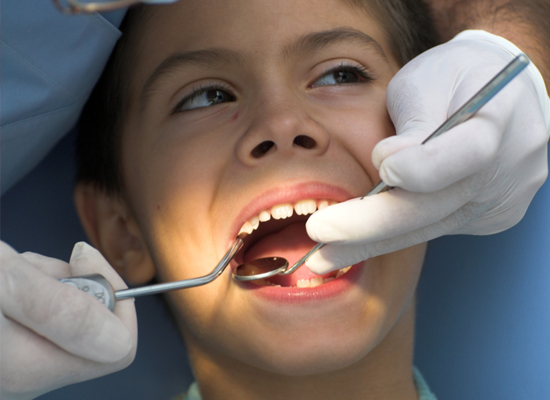
routine go to the dentist. If you don’t visit your dentist on a regular basis, you might not be aware of dental issues until they cause serious harm because the majority of dental disorders are painless at first. Get regular dental checkups every six months for optimal outcomes, or more frequently if you have a higher risk of oral illnesses. Oral cancer screenings should be performed by your dentist to look for indications of aberrant tissues. Dental examinations should include a review of the growth and development of the mouth, particularly in youngsters, as well as a caries development assessment.
Instruction for patients. Patients are more likely to visit their dentist for preventative dentistry procedures if they are aware of the consequences of poor oral health. A lifetime of good dental health is considerably increased by instilling good oral hygiene practices.
Types of Fluoride
Applying topical fluorides to teeth strengthens them and increases their resistance to decay. Toothpaste, mouthwash, and professionally applied fluoride treatments (gels, foams, rinses, or varnishes) are examples of topical fluorides. Children up to the age of 18 receive topical fluoride therapy from several dentists. Dentists may recommend a particular gel for regular usage at home in cases of excessive cavities or decay predispositions, such as those with dry mouth or orthodontic appliance wearers.
The body absorbs systemic fluorides, which then combine to build tooth structures. Because fluoride is found in saliva, which continuously moisturises teeth, systemic fluorides can also provide topical protection. Fluoride supplements in food form, such as pills, drops, or lozenges, or fluoridation of public water supplies are examples of systemic fluorides. But bear in mind that different regions may have different amounts of both naturally occurring and artificially added fluoride in their water supplies. To find out which type is ideal for your child in your location, speak with your child’s pedodontist.
Adults and kids two years of age and up are advised by the ADA to use fluoride toothpaste that has the ADA Seal of Acceptance on it. If you’re thinking about giving your child toothpaste before they turn two, speak with their dentist. Additionally, the ADA advises against using fluoride mouthwash on children younger than six years old due to the risk of swallowing the rinse.